Background
The Indian diet, with its emphasis on plant-based foods and limited consumption of fatty fish, can result in a relatively lower intake of omega-3 fatty acids compared to diets that prioritize fish consumption. However, it is essential to acknowledge that the Indian diet is diverse, and regional variations exist, with some regions incorporating fish and seafood into their cuisines, which can contribute to omega-3 intake.
In the traditional Indian vegetarian diet, omega-3 fatty acids are primarily derived from plant-based sources like flaxseeds, chia seeds, walnuts, and certain oils like mustard oil. These foods provide alpha-linolenic acid (ALA), a type of omega-3 fatty acid that can be converted to the more biologically active forms, eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA), and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), although the conversion rate is typically low.
However, the consumption of these omega-3-rich plant-based foods may vary among individuals and regions in India. Additionally, traditional cooking methods involving high-temperature cooking and the use of excessive oil can further impact the availability of omega-3s in cooked dishes.
Considering the relatively low intake of omega-3s in the Indian diet, supplementation can serve as a convenient and reliable source, especially for individuals who do not consume fish regularly or have dietary restrictions.
Omega-3 supplementation can help restore the balance between omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids, which are often imbalanced in modern diets. Furthermore, high-quality omega-3 supplements undergo purification processes to minimize contaminants such as mercury, PCBs, and dioxins, addressing concerns about consuming contaminated fish.
It is important to note that specific health conditions, such as high triglyceride levels, cardiovascular disease, rheumatoid arthritis, and depression, have established benefits associated with omega-3 fatty acids. Pregnant women, infants, and young children may also benefit from omega-3 supplementation to support proper development.
Omega-3 fatty acids supplementation can help bridge the gap and provide essential nutrients that support overall health and well-being. However, dietary choices, cultural practices, and individual needs should be considered, and consulting with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian is recommended for personalized advice.
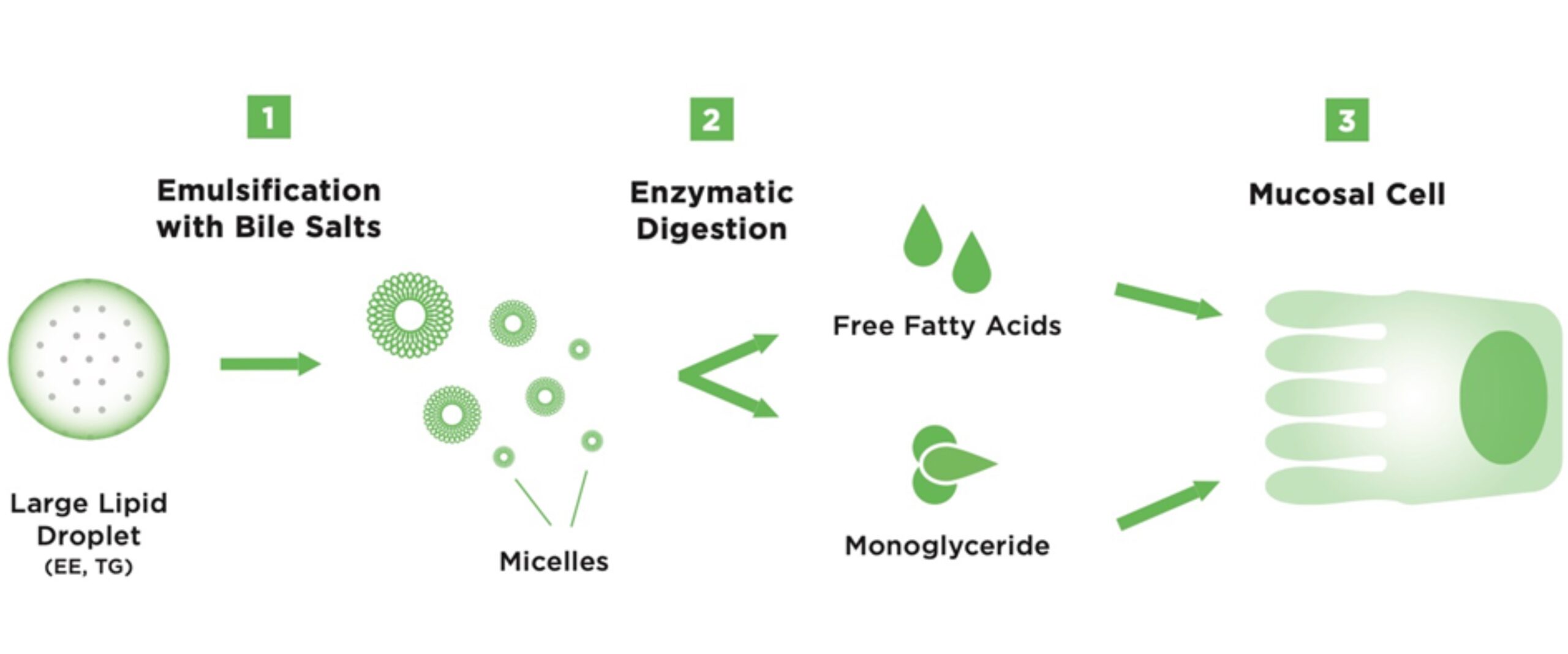
Currently USP omega-3 in the market is the form of large lipid molecules i.e TG and EEs which has to be broken down into MG by enzymes for its absorption into the system. This process takes a longer time resulting in excretion of these molecules without getting absorbed. Hence omega-3 is needed to be taken in larger doses which further leads to problems like digestive discomfort and fishy burps.
How do we digest Omega-3 fatty acids?
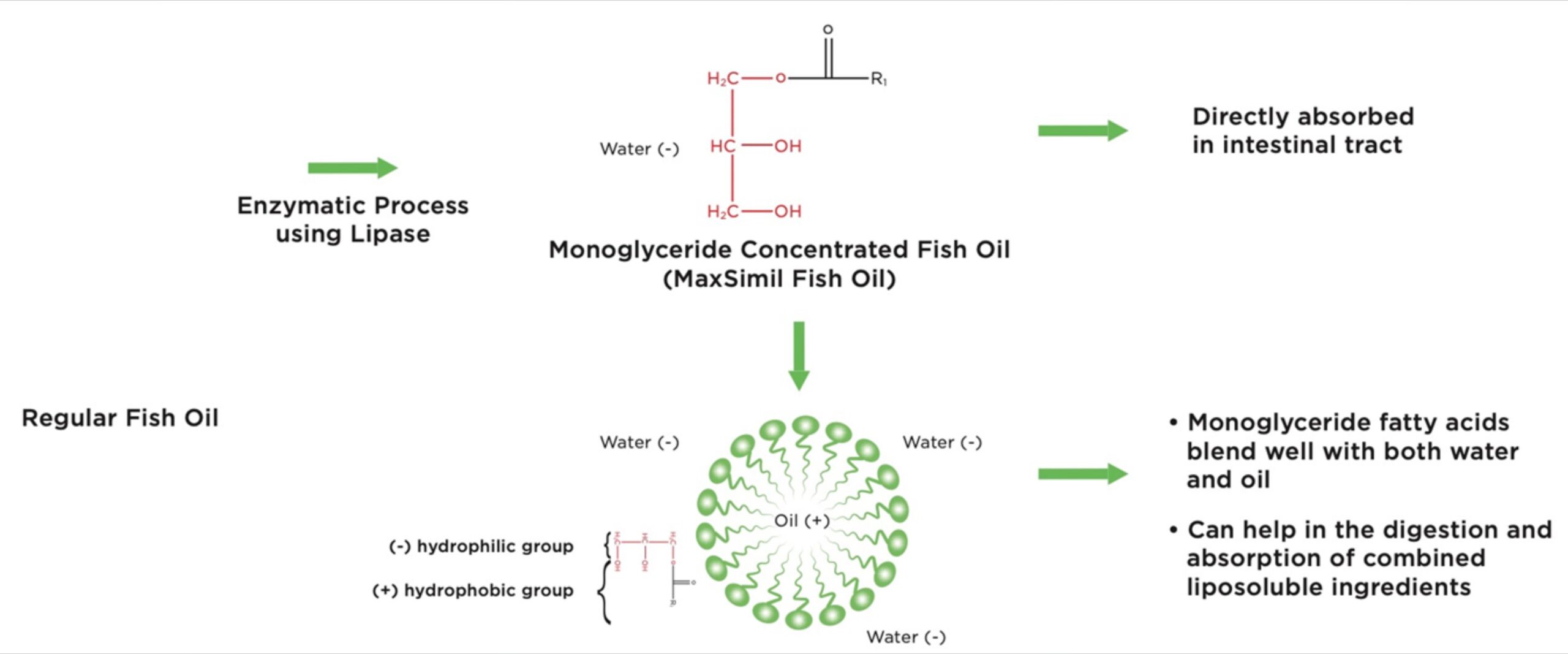
What is MaxSimil®
Maxsimil, patented lipid absorption technology is a novel delivery system that enhances the absorption of omega-3 fatty acids and other lipid-based active agents. It mimics the natural human enzymatic process, using a patented monoglyceride-rich fish oil to deliver EPA and DHA and maximize their absorption. The omega-3 fatty acids are readily absorbable in the form of small emulsifying molecules that can be directly assimilated in the intestinal tract.
This unique platform can also acts as a natural, delivery system for nutraceutical ingredients, increasing the absorption of combined fat-soluble micronutrients such as CoQ10. It’s an excellent method for delivering omega-3 fatty acids to individuals with compromised digestion due to age, health and/or medication.
Key Benefits
- More omega-3s faster and better absorbed
- Smaller and fewer softgels per day
- No additional ingredients/excipients required for enhanced benefits
- 100% fish oil, no dilution
Mechanism of Action
applications

Supports Heart Health

Supports Brain Health



